Pet Communication: Understanding How Your Pets Express Emotions and Needs
Pets communicate with us every day, but their signals are often subtle and easy to miss. Pet communication involves body language, sounds, and behaviors that convey emotions, needs, and intentions. Learning to interpret these cues strengthens your bond, prevents misunderstandings, and ensures better care.
In this guide, we’ll break down:
- How dogs express themselves through understanding dog communication.
- What cat body language explained reveals about their feelings.
- The many ways pets show affection.
- Key tips for decoding pet behavior signals in different situations.
Let’s dive in.
Understanding Dog Communication
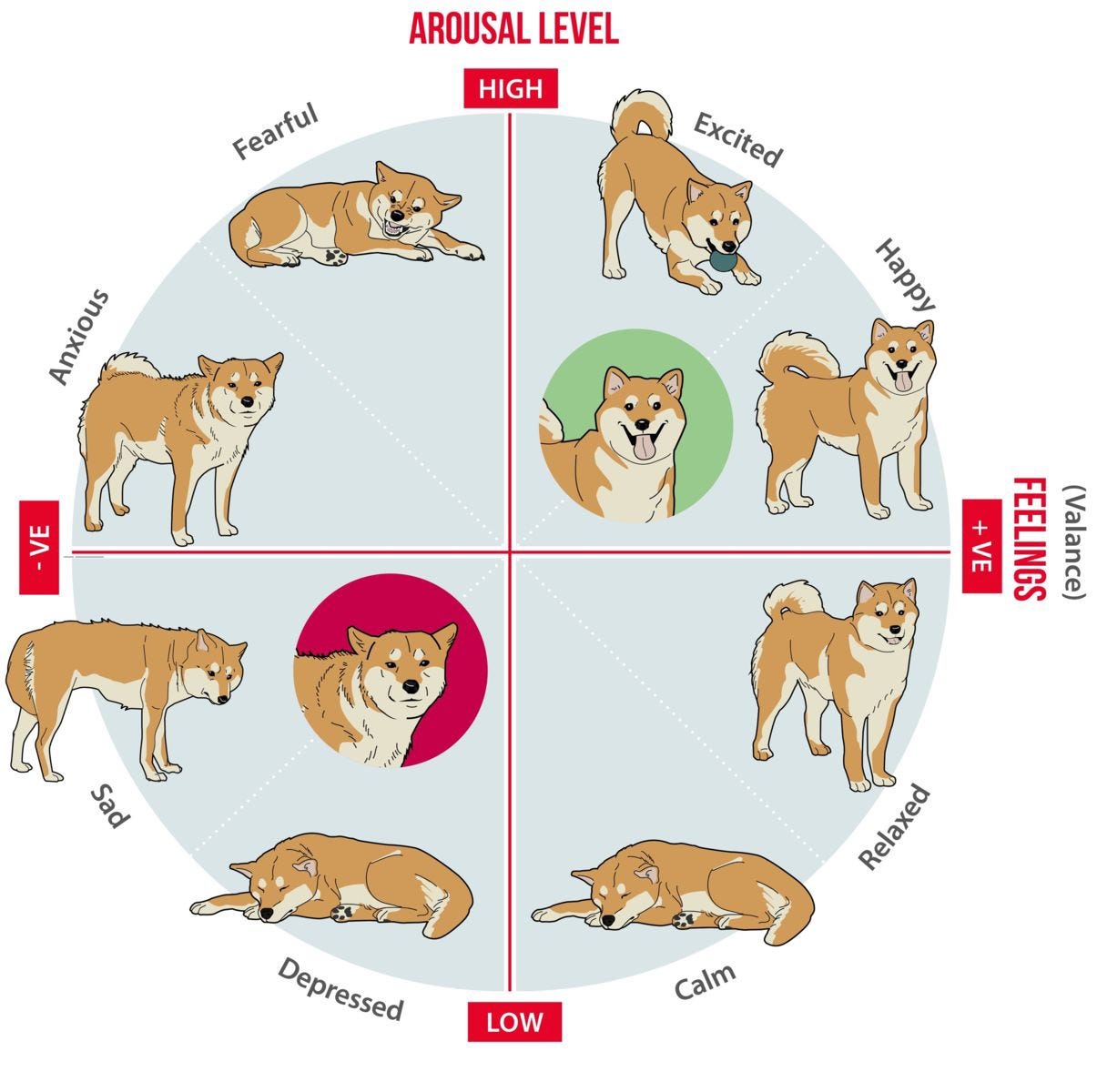
Dogs use body language, vocalizations, and actions to express themselves. Here’s how to read their signals.
Dog Body Language
- Tail movements:
- High, fast wagging = excitement.
- Slow, low wagging = uncertainty.
- Tucked tail = fear or submission. (Source: AKC)
- Ears:
- Forward = alert or curious.
- Pinned back = anxiety or fear.
- Posture:
- Play bow (front down, rear up) = invitation to play.
- Stiff, raised hackles = aggression or discomfort.
Dog Vocalizations
- Barking:
- Short, sharp barks = alert (e.g., doorbell).
- Prolonged barking = boredom or distress.
- Whining:
- High-pitched = stress or attention-seeking. (Source: DCC Pets)
- Growling:
- Low growl = warning (give space).
Common Misinterpretations
- Rolling over:
- Can mean submission, not always a belly rub request.
- Yawning:
- Often a stress signal, not just tiredness.
For more on how dogs perceive the world, check out How Dogs See the World: Exploring Their Unique Sensory Perception.
Cat Body Language Explained
Cats communicate quietly but clearly through posture, tail movements, and sounds.
Cat Tail Signals
- Upright tail: Happy or confident.
- Puffed-up tail: Fear or aggression.
- Thrashing tail: Irritation. (Source: Humane Society)
Eyes & Ears
- Ears:
- Forward = content.
- Flattened = angry or scared.
- Eyes:
- Slow blinks = trust (try blinking back!).
- Dilated pupils = excitement or fear. (Source: PetMD)
Cat Vocalizations
- Purring:
- Usually contentment, but can indicate pain (check context).
- Hissing:
- Fear or aggression—give space.
- Meowing:
- Mostly directed at humans (varies by tone).
How Pets Show Affection
Both dogs and cats have unique ways of expressing love.
Dog Affection Signs
- Licking: A grooming behavior showing trust.
- Leaning: Seeks closeness and security. (Source: Community Animal Hospitals)
- Bringing toys: A “gift” for their favorite human.
Cat Affection Signs
- Head-butting (bunting): Scent-marking to bond.
- Kneading: A kitten-like behavior showing comfort.
- Sleeping near you: A sign of deep trust.
Subtle Signs of Love
- Following you around.
- Gentle nibbling (cats) or “smiling” (dogs).
Decoding Pet Behavior Signals
Context matters—learn to spot stress, playfulness, and aggression.
Stress Indicators
- Dogs: Pacing, excessive panting, avoiding eye contact.
- Cats: Over-grooming, hiding, sudden aggression. (Source: RSPCA)
Play vs. Aggression
- Dogs:
- Play = loose, wiggly movements.
- Aggression = stiff posture, raised hackles.
- Cats:
- Play = crouched wiggle before pouncing.
- Aggression = arched back, puffed fur.
Why Context Matters
A wagging tail in a noisy park may mean nervousness, not happiness. Always observe the full situation. (Source: AKC)
For more on how dogs adapt to low-light conditions, read What Do Dogs See at Night? Exploring Canine Night Vision.
Conclusion
Pet communication is a mix of body language, sounds, and behaviors. By understanding dog communication and cat body language explained, you can respond better to their needs.
Key Takeaways:
- Watch tail, ear, and posture cues.
- Learn their vocalizations (barks, meows, purrs).
- Notice subtle signs of affection.
Practice daily: Spend time observing your pet’s unique signals.
Now it’s your turn! Share in the comments—how does your pet communicate with you?
Additional Tips
- Visual aids: Use labeled images of tail/ear positions for clarity.
- Keyword use: Naturally include terms like “pet behavior signals” and “feline communication.”
By mastering pet communication, you’ll build a happier, healthier relationship with your furry friend!
For more insights into dog-friendly foods, check out Can Dogs Eat Sauerkraut? and Can Dogs Drink Almond Milk?.
FAQ
Q: How can I tell if my dog is stressed?
A: Look for pacing, excessive panting, or avoidance of eye contact. These are common signs of stress in dogs.
Q: Why does my cat knead me with its paws?
A: Kneading is a kitten-like behavior that shows comfort and affection, often indicating they feel safe with you.
Q: Is a wagging tail always a sign of happiness in dogs?
A: Not always. Context matters—a slow, low wag can indicate uncertainty, while a stiff, high wag may signal alertness or aggression.
